A CONSUMER'S GUIDE TO ELECTRIC VEHICLES
Why Make the Switch?
Here are just a few of the many benefits electric vehicles bring to consumers.
Lower Operation Costs—The operation costs of an electric vehicle are on average about half the cost compared to an internal combustion vehicle. Fueling your car with electricity is significantly less expensive as well. Electricity rates can cut fuel costs down to a third what a consumer pays annually for gasoline.
Environmentally Friendly— All-electric vehicles produce no tailpipe emissions. Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV) produce no tailpipe emissions, when in electric mode. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, a typical passenger vehicle with an internal combustion engine emits 4.6 metric tons of carbon dioxide per year. Electric vehicles produce about a third of this at the power plant level.
EV Performance Benefits— Electric vehicles are quiet, provide a higher torque output, provide superior traction control and require far less maintenance than an internal combustion vehicle.
Three types of electric vehicles
From all electric to hybrid, there's an EV for every driving style.
 Hybrid Electric Vehicles—HEV’s have both an internal combustion engine, and an electric motor. HEV’s do have batteries, but the main energy source is gas. HEV’s do not have plug-in capability. The battery is charged by regenerative braking and by the gas-powered engine.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles—HEV’s have both an internal combustion engine, and an electric motor. HEV’s do have batteries, but the main energy source is gas. HEV’s do not have plug-in capability. The battery is charged by regenerative braking and by the gas-powered engine.
 Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles—PHEV’s have both an internal combustion engine, and an electric motor. The majority of the energy used to drive the vehicle is electricity. These vehicles typically have smaller gas powered engines, and larger battery storage compared to HEV’s. These vehicles can run strictly on electricity or switch to gas when battery storage is running low. PHEVs also have plug-in capabilities to charge the battery directly.
Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles—PHEV’s have both an internal combustion engine, and an electric motor. The majority of the energy used to drive the vehicle is electricity. These vehicles typically have smaller gas powered engines, and larger battery storage compared to HEV’s. These vehicles can run strictly on electricity or switch to gas when battery storage is running low. PHEVs also have plug-in capabilities to charge the battery directly.
 All Electric of Battery Electric Vehicles—Electric vehicles use the energy stored in their high capacity onboard batteries to power the car. EV batteries are charged by plugging into an electric power source to charge the batteries directly.
All Electric of Battery Electric Vehicles—Electric vehicles use the energy stored in their high capacity onboard batteries to power the car. EV batteries are charged by plugging into an electric power source to charge the batteries directly.
Three levels of charging stations
The levels represent the speed at which the EV battery can be fully charged. There are also four different types of charging ports. The charging stations and ports are as follows:

-
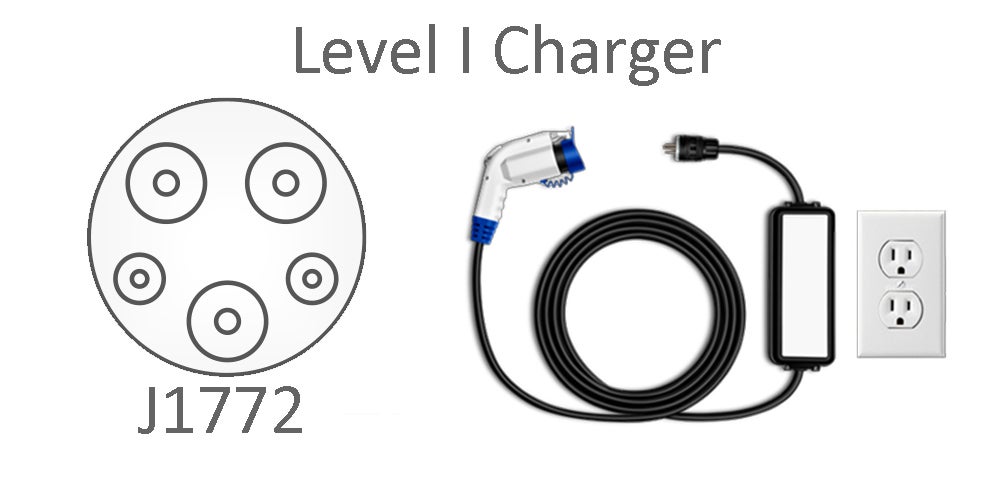
Level I (Cost: $200 - $450)
-
Charges 2-5 miles per hour
-
The standard charge port is a J1772 port. With a level 1 charger the other end would be a standard 3 prong 120 outlet.

-
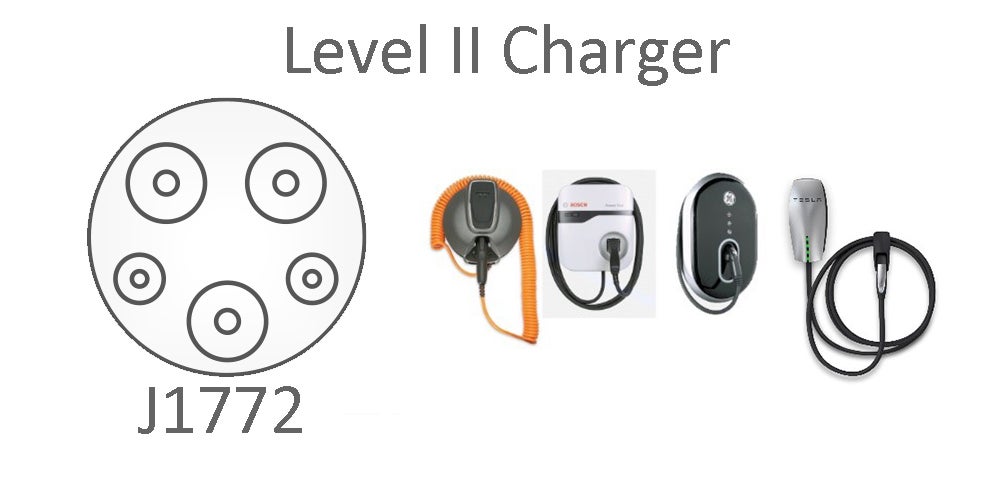
Level II (Residential: $400 - $1,000 /Commercial: $4,000 - $7,000)
-
Charges 10-20 miles per hour
-
The standard charge port for a level II charger is still the J1772 port, but the other end is a 240 volt connection.
-
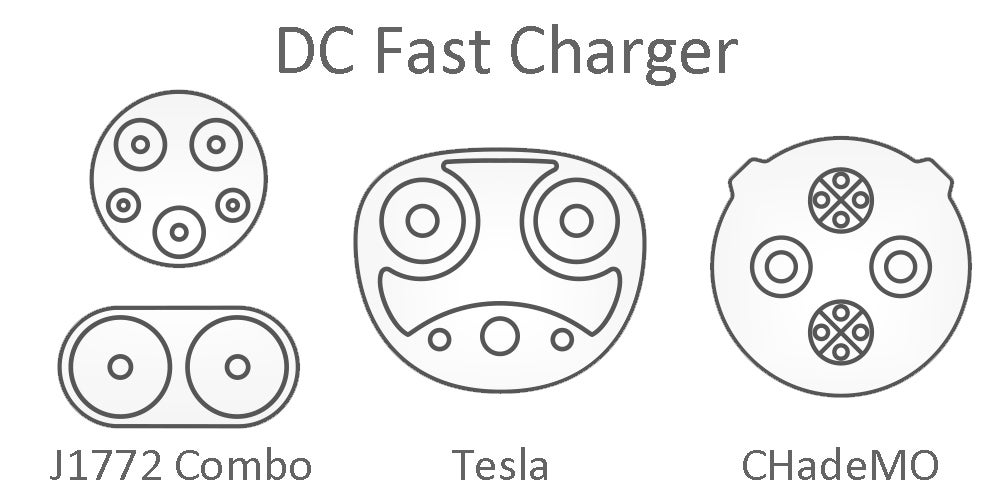
DC Fast Charge ( $12,000 - $35,000)
-
Charges 60-100 miles in 20 min
-
There are three main types of charge ports for DC fast chargers. The first is the J1772 combo. This can be used for levels I, II, and DC fast charging stations. The second is the CHadeMO, which is used for mostly Nissan and Toyota vehicles. Finally, the Tesla has its own unique charge port that works for their supercharger stations.


